This guide will show the basic setup of K8s using GCP storage disk.
Our goal here is to have a pod use storage for the external disk in GCP (Google Cloud Platform) using persistent volume and persistent volume claim. See this diagram for example.
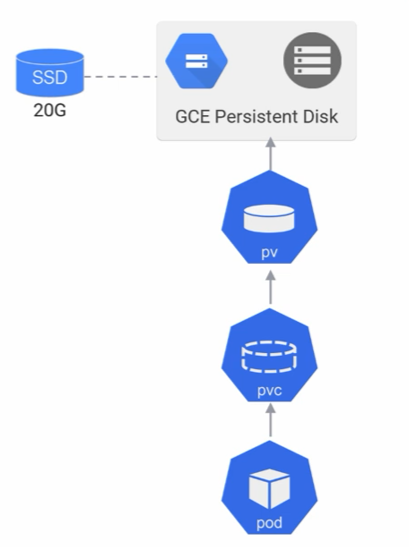
PV (Persistent Volume) and PVC (Persistent Volume Claim)
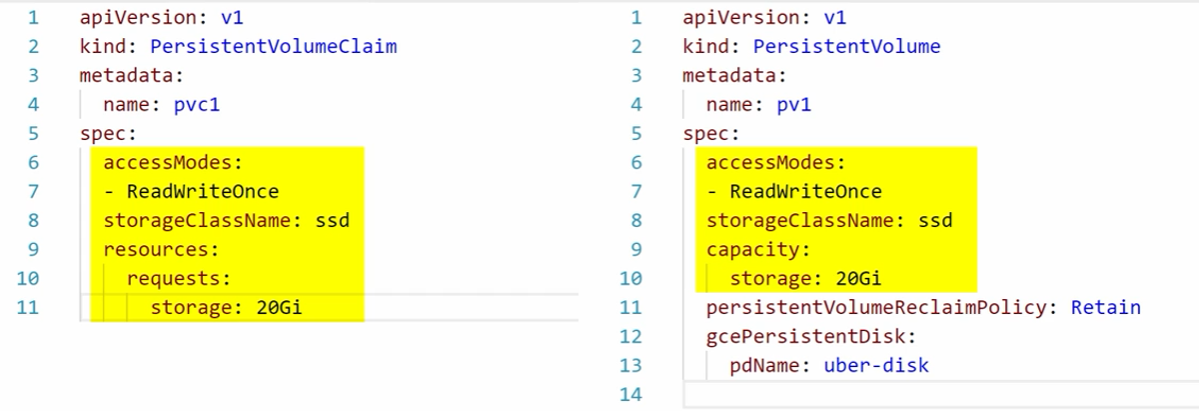
Below is the manual process of creating both PV (Persistent Volume) and PVC (Persistent Volume Claim)
Note: PVC and PV need to match the following:
- Access modes
- Storage class name
- Storage size
Steps to achieve this:
Create a disk in GCP
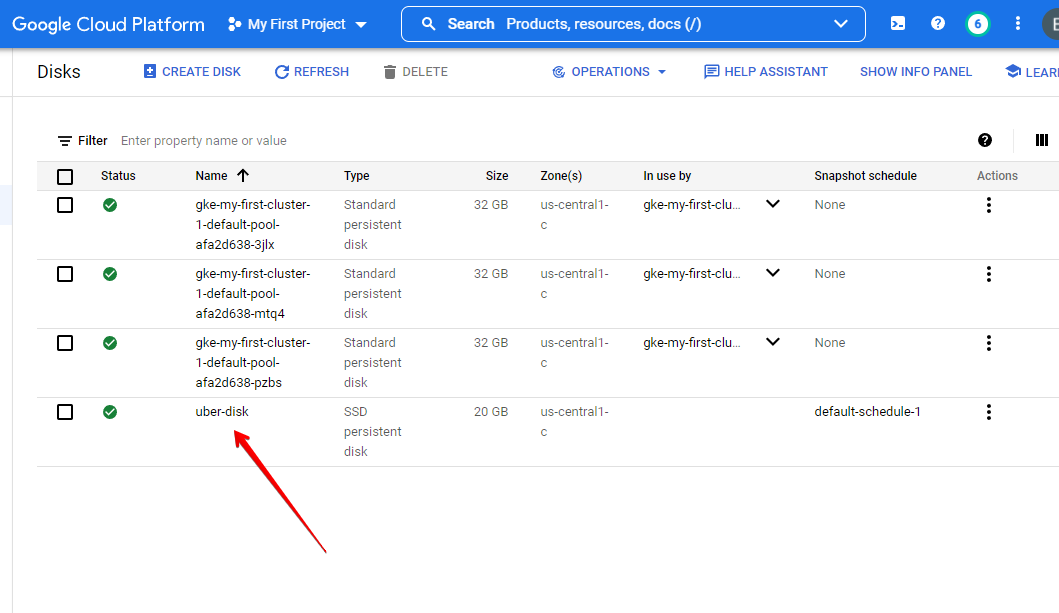
Create the PV yaml resource file
gke-pv.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: ssd
capacity:
storage: 20Gi
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
gcePersistentDisk:
pdName: uber-diskApply the pv yml file.
kubectl apply -f gke-pv.yml 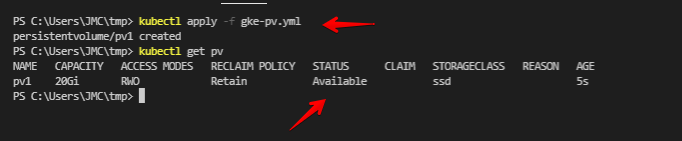
Create the PVC yml resource file
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: ssd
resources:
requests:
storage: 20GiApply the PVC yml file
apply -f gke-pvc.yml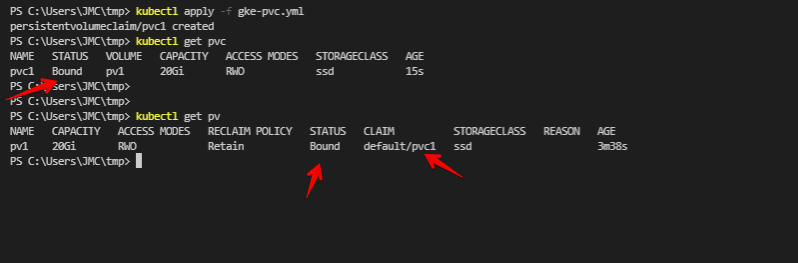
pv1 and get pv shows that the pv1 claimed by pvc1Note: a PVC storage size is larger than the PV storage size, it will not work and the status will remain pending
Create a pod using that PVC claim from the 20GB PV
Apply the gke-podvol.yml
kubectl apply -f gke-volpod.yml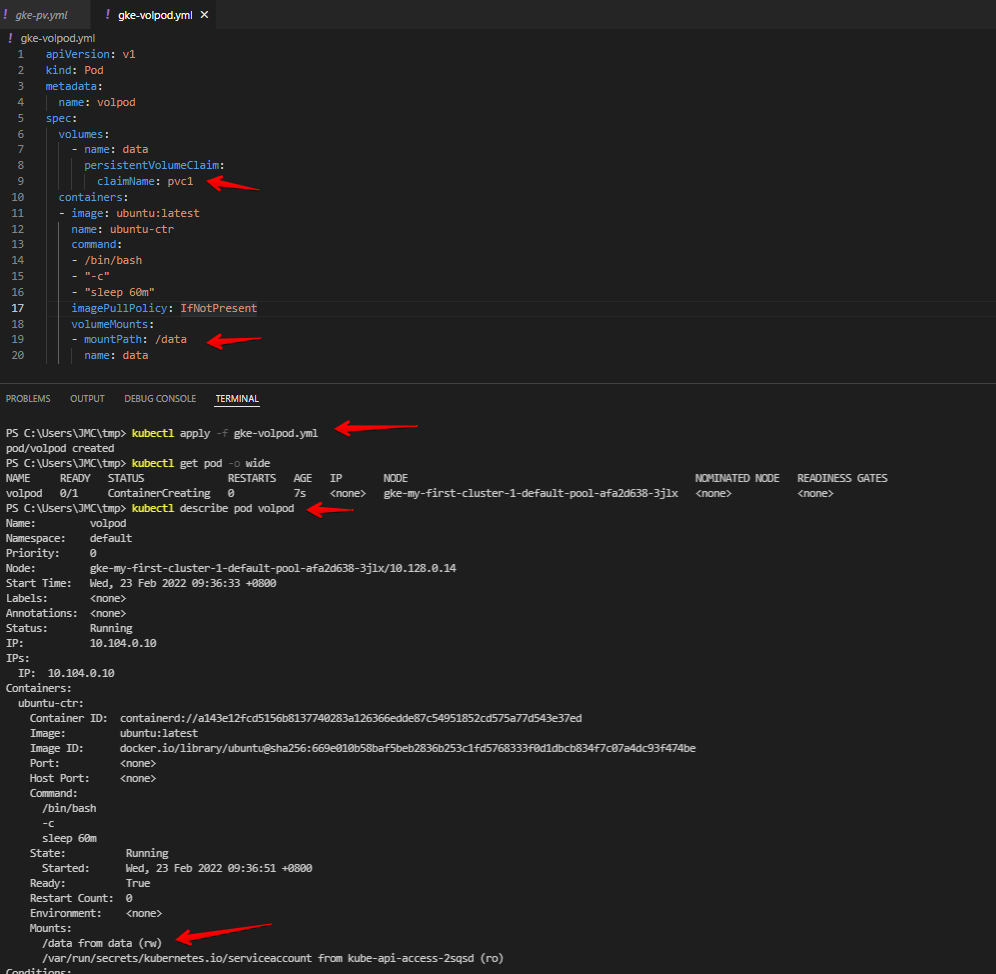
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: volpod
spec:
volumes:
- name: data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc1
containers:
- image: ubuntu:latest
name: ubuntu-ctr
command:
- /bin/bash
- "-c"
- "sleep 60m"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: dataSSH to the pod we created and check the disk space that shows the volume we created (data)
kubectl exec -ti volpod -- bash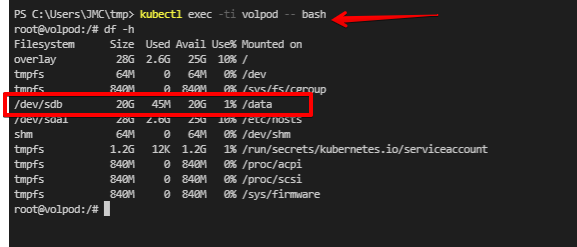
Storage Class (dynamic way)
This is the part where we don’t need to create a PV manually like the first step above. In this method:
- Storage class
standtardwas automatically created by GKE - Anytime a new PVC comes asking for storage targeting the SC
standard, it dynamically creates it on the back end. - Create the PV on the cluster.
When you create a cluster in GCP (GKE – Google Kubernetes Engine), it automatically creates a storage class. Check this link https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/concepts/persistent-volumes
GKE creates a default
StorageClassfor you which uses the standard persistent disk type (ext4). The defaultStorageClassis used when aPersistentVolumeClaimdoesn’t specify aStorageClassName.
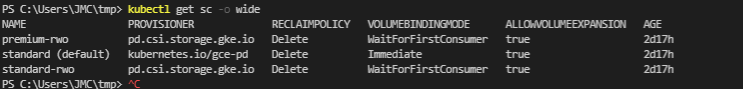
The link above also says:
When defining a
StorageClass, you must list a provisioner. On GKE, we recommend that you use one of the following provisioners:
So the screenshot above that says premium-rwo is the Compute Engine PD CSI
This is what the YAML of that SC looks like:
PS C:\Users\JMC\tmp> kubectl get sc premium-rwo -o yaml
allowVolumeExpansion: true
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
annotations:
components.gke.io/component-name: pdcsi
components.gke.io/component-version: 0.11.5
components.gke.io/layer: addon
creationTimestamp: "2022-02-20T08:10:47Z"
labels:
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: EnsureExists
k8s-app: gcp-compute-persistent-disk-csi-driver
name: premium-rwo
resourceVersion: "339"
uid: 44c6d6a8-e6d3-4736-a761-587f56769042
parameters:
type: pd-ssd
provisioner: pd.csi.storage.gke.io
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumerScreenshots below we created a PVC called pvc-custom from an existing storage class provided by GKE called standard and it also shows in GKE console.
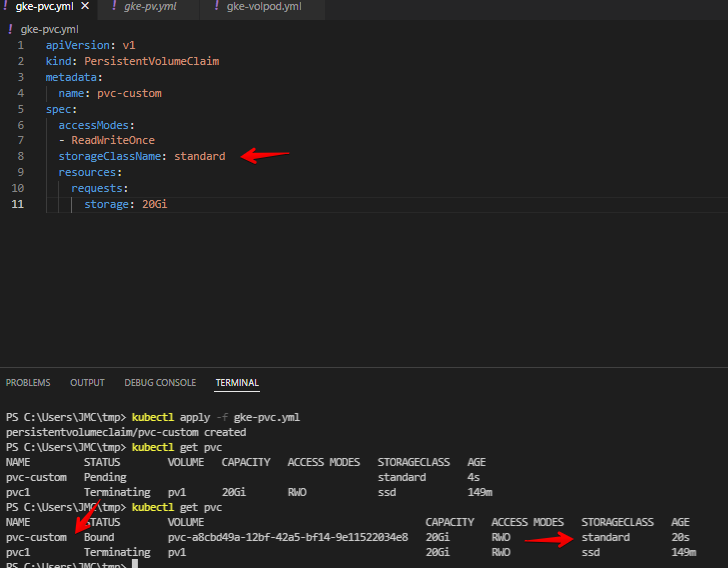
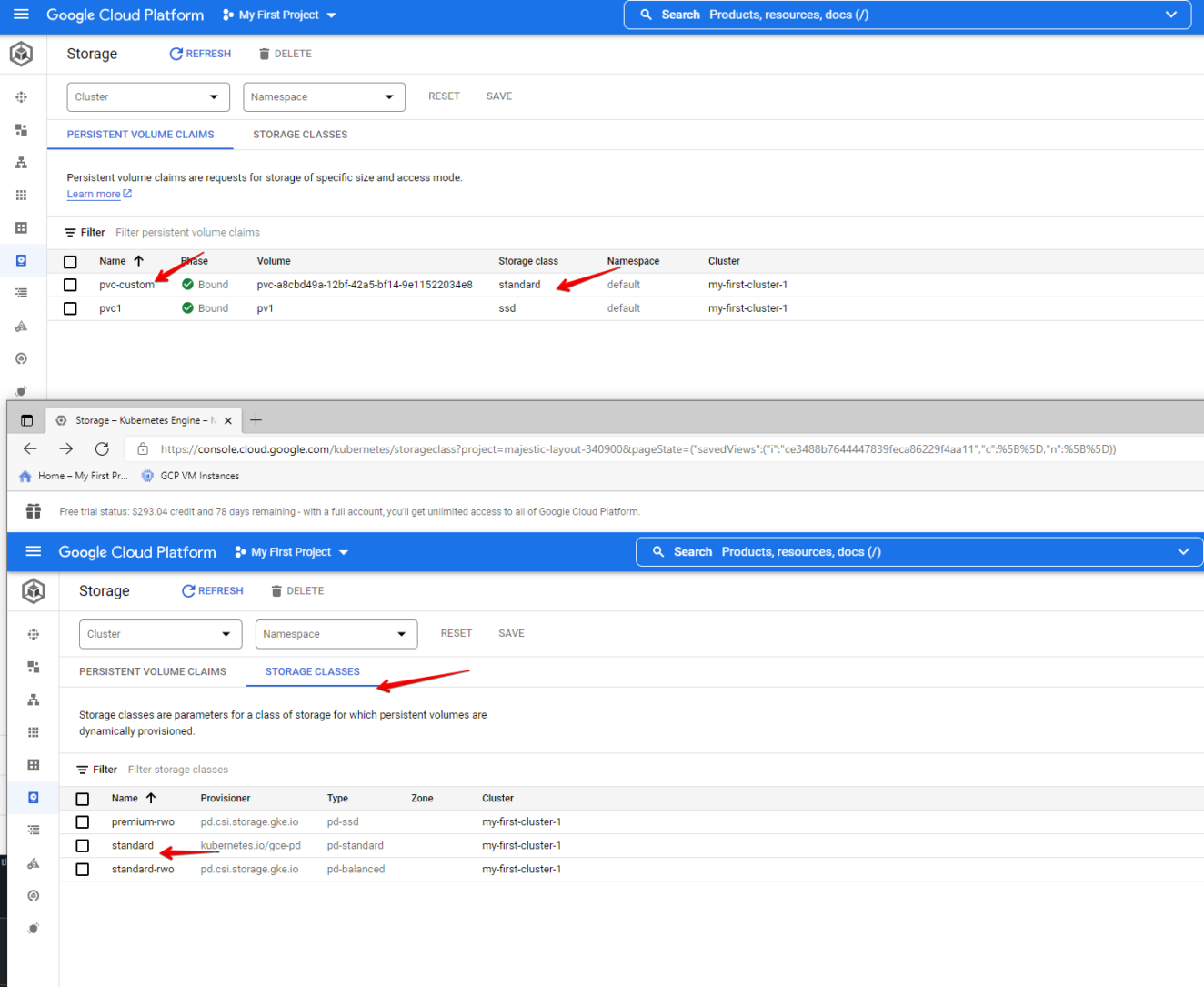
Another SC example.
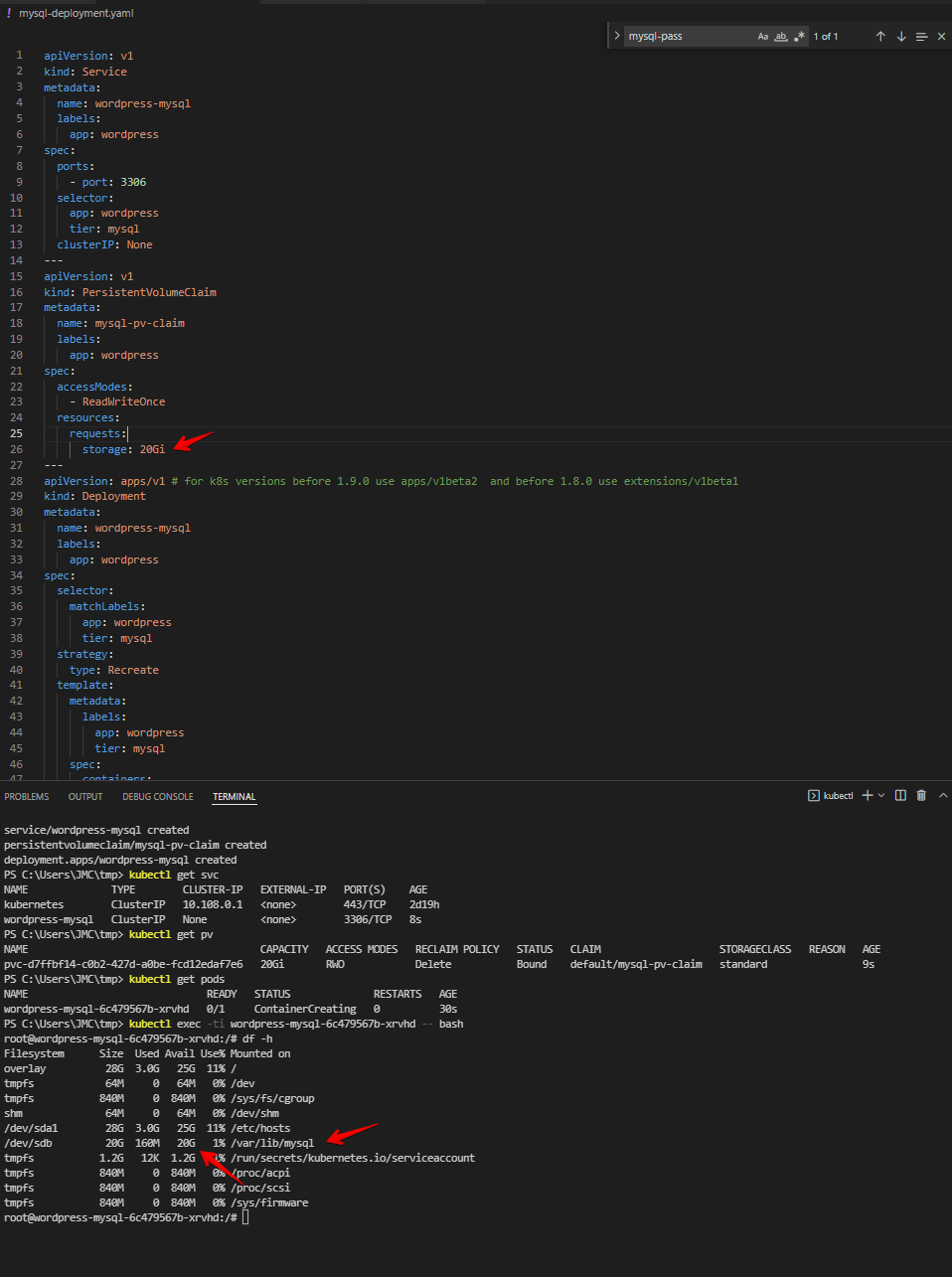
Below it creates:
- Password for our mysql deployment
- Applying the deployment yml file that creates:
- A service with port 3306
- a PVC name
mysql-pv-claimwith 20GB size - Deployment with mysql image that:
- uses the password using from kubectl create secret
- mounts to /var/lib/mysql
- targets the PVC called
mysql-pv-claim
Create a secret password for mysql
kubectl create secret generic mysql-pass --from-literal=password=Password123Applying mysql-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f .\mysql-deployment.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: wordpress-mysql
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
ports:
- port: 3306
selector:
app: wordpress
tier: mysql
clusterIP: None
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mysql-pv-claim
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1 # for k8s versions before 1.9.0 use apps/v1beta2 and before 1.8.0 use extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: wordpress-mysql
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: wordpress
tier: mysql
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: wordpress
tier: mysql
spec:
containers:
- image: mysql:5.6
name: mysql
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysql-pass
key: password
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
name: mysql
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
volumes:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mysql-pv-claim